The 12th generation of Intel processors is rumored to arrive somewhere in the second half of 2021. Powering this generation will be the Alder Lake-S architecture from Intel. Since we’re currently on the 10th generation of intel processors that means that between the two, there will also be the 11th gen of CPUs. This generation of consumers use general CPUs from intel is called the Rocket Lake-S.
Rocket Lake-S CPUs will launch somewhere in late 2020 or the first quarter of 2021. It is built upon the 14nm+++ process. Interestingly Intel is still using the 14nm process. You can also notice that it is precisely the same as last time. Regardless of the manufacturing process, the Rocket Lake will feature Willow Cove nuclei, which gives it higher performance and efficiency.
Compared to the Comet Lake processors, this generation has more instructions per cycle. This explains the better performance at the same number of Cores and CPU clock speed. Since this is an advancement, Intel should have given this generation and additional “+” in the process naming. Who knows the company might be saving it for something big.
As mentioned earlier, the Rocket Lake-S should drop near the end of this year as we know that intel plans to launch processors built on 10nm technology in 2021. Intell will use 10nm technology in all of its products ranging from consumer CPUs to High-Performance electronics.
Also Read: Intel Stock shortage to end by 2023
More on Alder Lake:
Intel will use big.LITTLE structure in this generation. It is a widespread CPU structure in smartphones these days, and we have also seen instances of it in the x86 processors as well. This divides the core block into two significant groups. One performs higher while the other has slightly lower performance. Hence there will be a high-performance one formed by Core nuclei (Golden Cove) and a lower performance one formed by Atom nuclei (Gracemont).

This scheme from Intel is similar to what we have seen in the past. In the Lakefield CPUs, we had a 1-4 core division. Where there were four power-saving cores and a single high-performance core in the processor. The power-saving cores took care of redundant tasks of operating system and applications while the high-performance one kick in for more demanding workloads.
This time, however, the leaks suggest that we will see a higher number of cores in the CPU. This time intel will start at two cores and will go as high as sixteen cores in the chip. The picture below sheds light on expected core configurations in the next generation. We see the Alder Lake-S (desktop) and Intel Alder Lake-P (portable) processors, as well as the number of high performance and power-saving cores for each variant.
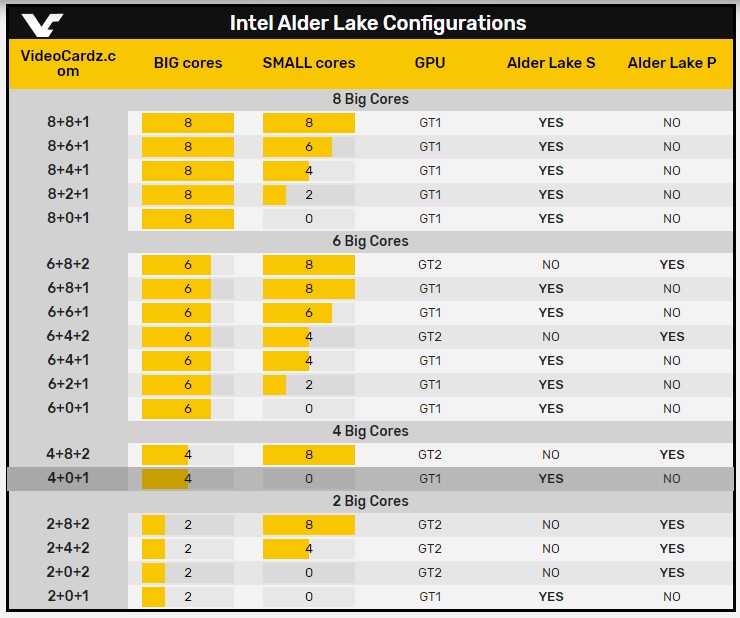
We can see from the above details that intel plans to make processors with eight, six, four, and even two high-performance cores, which will be paired with eight, six, four, or two low consumption cores depending on the model. In addition, some processors in the list don’t have low power cores.
While the eight-core models go in demanding machines in most of the mid-range consumer devices, we will expect the six core variants of this generation. You can think of the six-core CPU as an upgrade version of our i5 10600K using that reference; we can quickly evaluate the rest of the choices.
Another exciting device configuration in this image is an ALder Lake-P chip for mobile devices. This specific model has two high-performance cores and eight low power cores, which gives an exciting performance and use case scenario. Along with this new core configuration also has a high-performance integrated GPU GT2.
One thing to note, though is that the Alder Lake-S processor generation will use a newer LGA1700 socket; hence to use these processors, users will also need a motherboard upgrade.


