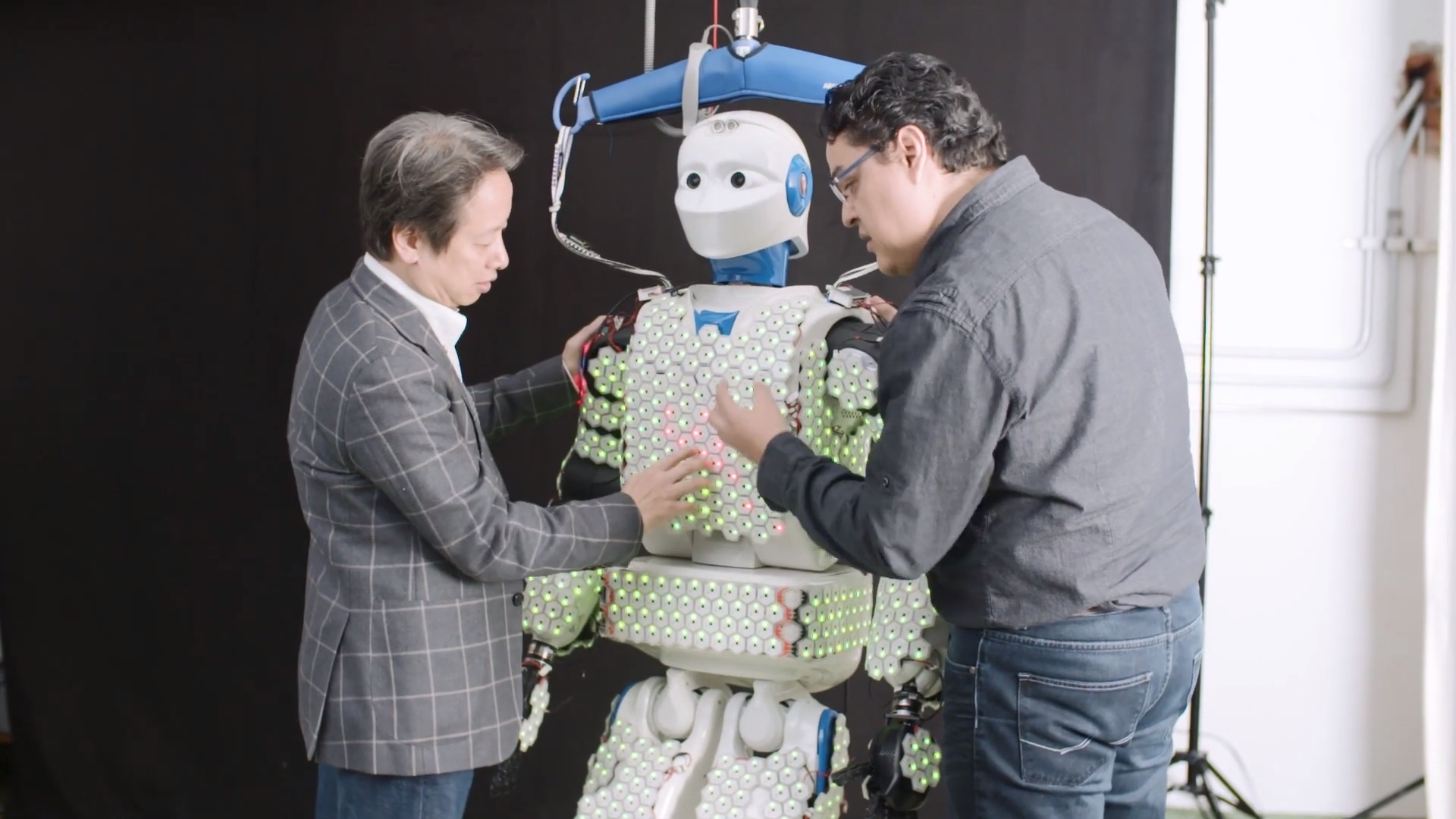
The human skin is an integral part of our existence and personality. It is what alerts us of dangers and protects us from god knows how many microorganisms. Learning from the crucial part it plays in human life. A team from The Technical University of Munich (TUM) has developed a robot equipped with a body covered in artificial skin. The robot pairs a ton of sensors with some control algorithms to run. The new skin technology takes us a step further helping robots to become aware of their surroundings.
One of science’s main goals is to replicate the Human body. It is one of the natures most sophisticated designs that couples many systems to achieve a living being. We have conquered in making machines that can walk like us and speak like us. However, the big challenge right now is developing consciousness and a neural system like humans. The new robot equipped with artificial skin is a big step as it brings the journey one step closer to humans.
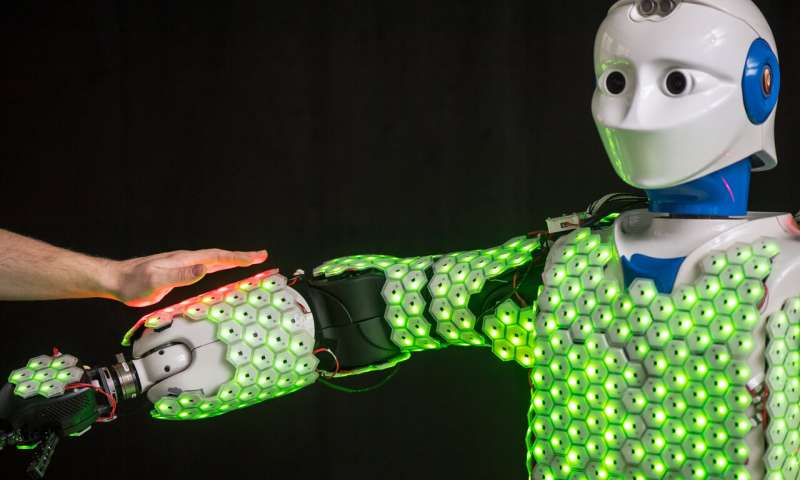

In addition to being closer to humans, a well sensed robot also means better safety functions. With the artificial skin, the new robot is able to navigate its environment better than ever. This will also come in useful to avoid some distance checks to stop robots from making contact with surfaces and objects. Which will be useful in preventing several accidents.
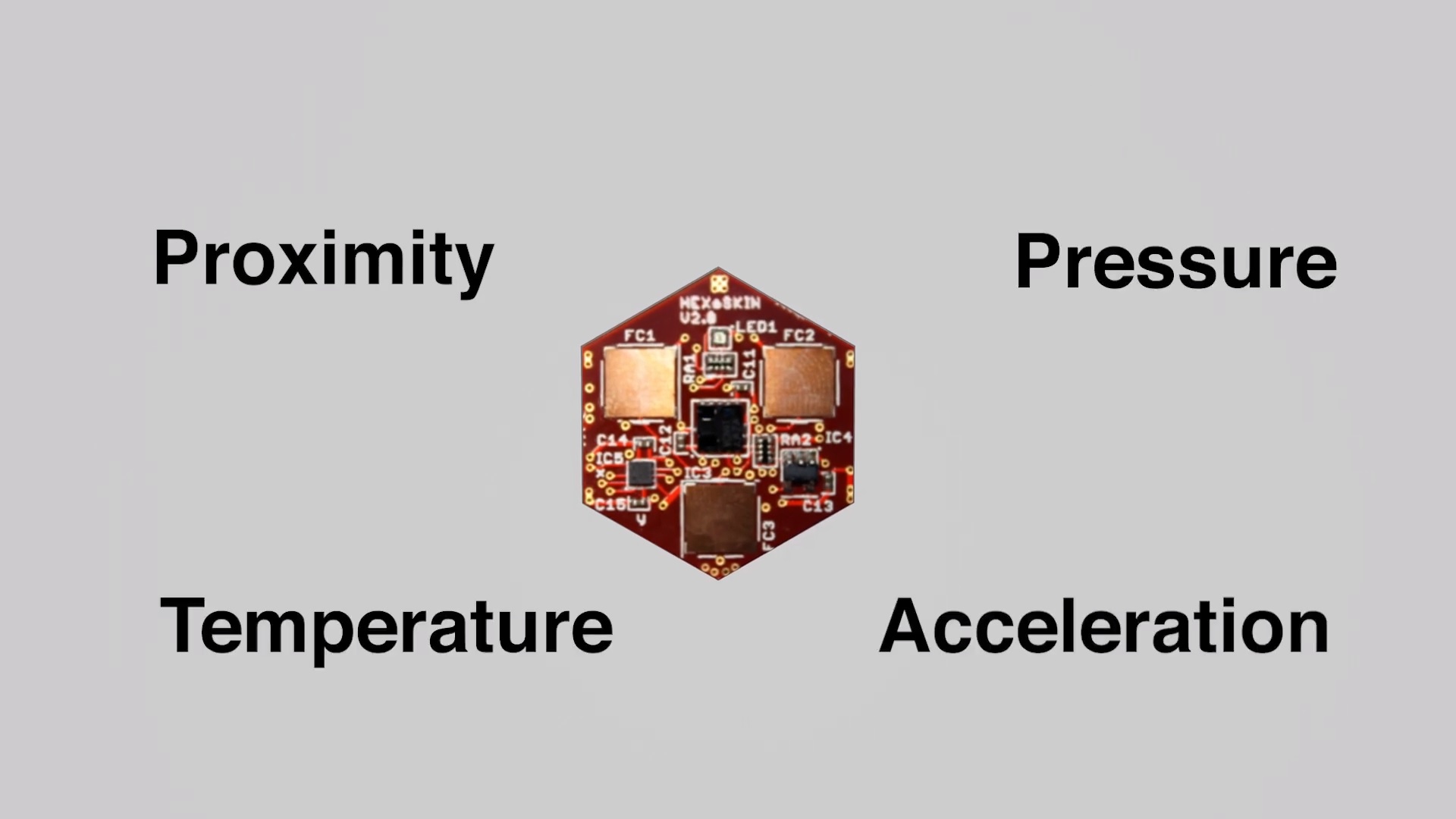
Small hexagonal cells each about one inch in diameter make up this artificial skin. Every hexagonal cell on the robot has a separate microprocessor. In addition to an array of sensors detect various things like contact, acceleration, proximity, and temperature.
Also read: Robot Can Now Store Energy like Humans.
The Team:
Prof. Gordon Cheng heads the team behind the innovative robot. He developed the actual skin technology a long time ago but it has taken them this long to actually implement it in a body. The amount of sheer processing power required to process data from all the sensors in this machine is one of the main hiccups the team faced in this journey. For Instance, the average human skin has about 5 million receptors. It is impossible to recreate that amount of robots even with today’s processor standards.
The input data in these systems is too much to get closer to realtime calculations and overloads the system instantaneously. In the recent developments, the team at TUM took the previous processing load down to 10 percent of its original value. They did this by developing an algorithm that does not require them to monitor sensor values at all times. The new algorithm instead only reads sensor data on specific events.
The latest robot using this artificial skin is named H-1 robot. It uses around 1260 of these hexagonal cells housing a total of Thirteen Thousand installed sensors. These sensors cover most of its upper body, arms, legs, and the soles of its feet. with this huge array of sensors, the H-1 can clearly sense the environment. Which gives it the ability to move along uneven surfaces and have better balancing.
Talking about his innovation Gordon Cheng explained that “This might not be as important in industrial applications. But in areas such as nursing care, robots must be designed for very close contact with people.”
The new development is very diverse and open doors for many innovations in the future. If we can make this cellular approach better it will even outperform conventional designs. Mainly because it can function when some of the cells are lost. Consequently, making our machines even more reliable.


